
Because the company has not created any real value simply by announcing a stock dividend, the per-share market price is adjusted according to the proportion of the stock dividend. Traders who look for short-term gains may also prefer dividend payments that offer instant gains. On top of that, retained earnings are ultimately the right of a company’s shareholders. This process adds the profits or losses to the retained earnings balance.

The Fundamental Accounting Equation
- Retained earnings are an equity account, appearing in the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet.
- Similarly, it denotes the shareholders’ rights to a company’s assets after liquidation.
- However, this creates a potential for tax avoidance, because the corporate tax rate is usually lower than the higher marginal rates for some individual taxpayers.
- Let’s say your company’s dividend policy is to pay 50 percent of its net income out to its investors.
Retained earnings are usually considered a type of equity as seen by their inclusion in the shareholder’s equity section of the balance sheet. Though retained earnings are not an asset, they can be used to purchase assets in order to help a company grow its business. Retained https://pharmalaneuk.bdccoder.in/what-is-501c3-status-and-why-does-it-matter/ earnings are affected by any increases or decreases in net income and dividends paid to shareholders.
FAQs About Retained Earnings Calculation
This accumulates over time, representing total historical profits held within the company. Retained earnings are calculated by taking the beginning retained earnings balance, adding net income or subtracting a net loss for the period, and then subtracting any dividends paid out. Retained earnings represent the cumulative are retained earnings liabilities net income of a company that has not been distributed to its shareholders as dividends. It is a component of shareholders’ equity, signifying an ownership claim on the company’s assets rather than an obligation owed to an external party.
What Is the Difference Between Retained Earnings and Dividends?

Other names for income are revenue, gross income, turnover, and the « top line. » There are times when company owners must invest their own money into the company. Intangible assets are things that represent money or value, such as accounts receivables, patents, contracts, and certificates of deposit (CDs).
- Organizing your expenses into specific budget categories helps you prepare for a smooth tax filing season and make more informed business decisions.
- CGAA will not be liable for any losses and/or damages incurred with the use of the information provided.
- This section indicates the company’s immediate financial commitments to outside parties.
- On the other hand, if you have net income and a good amount of accumulated retained earnings, you will probably have positive retained earnings.
- The remainder is the shareholders’ equity which would be returned to them.
Companies utilize retained earnings to strengthen their financial position, for example, by paying down debt or building cash reserves for unexpected challenges. This reinvestment aims to generate greater earnings, ledger account fostering long-term stability and growth. The decision to retain earnings or distribute them as dividends depends on the company’s growth opportunities and its overall financial strategy. While the basic accounting equation serves to summarize a company’s overall financial structure, the expanded version provides deeper insights into what drives equity changes.

Shareholders’ Equity
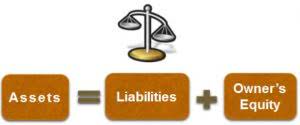
This placement within equity clearly distinguishes it from both assets and liabilities. Retained earnings represent the cumulative net income a business has generated, less any dividends distributed to its shareholders. These are profits that a company has chosen to keep within the business, rather than paying them out to owners or investors. The purpose of retaining these earnings is often to reinvest them back into the company for various strategic uses. On the other hand, retained earnings are the part of a company’s cumulative profit set aside for future use. They can be used for expansion or to pay dividends to shareholders later.
Comments are closed.